Absolutely! Here’s a 2500-word article on business architecture tools, formatted with `
` and `
` tags instead of “.
In today’s dynamic and competitive business environment, organizations are constantly striving to align their strategies with their operational capabilities. Business architecture serves as the crucial bridge between these two realms, providing a holistic view of the enterprise and enabling informed decision-making. To effectively implement business architecture, organizations rely on specialized tools that facilitate the creation, management, and analysis of architectural artifacts. This article explores the landscape of business architecture tools, examining their features, benefits, and considerations for selection.
The Foundation: Understanding Business Architecture
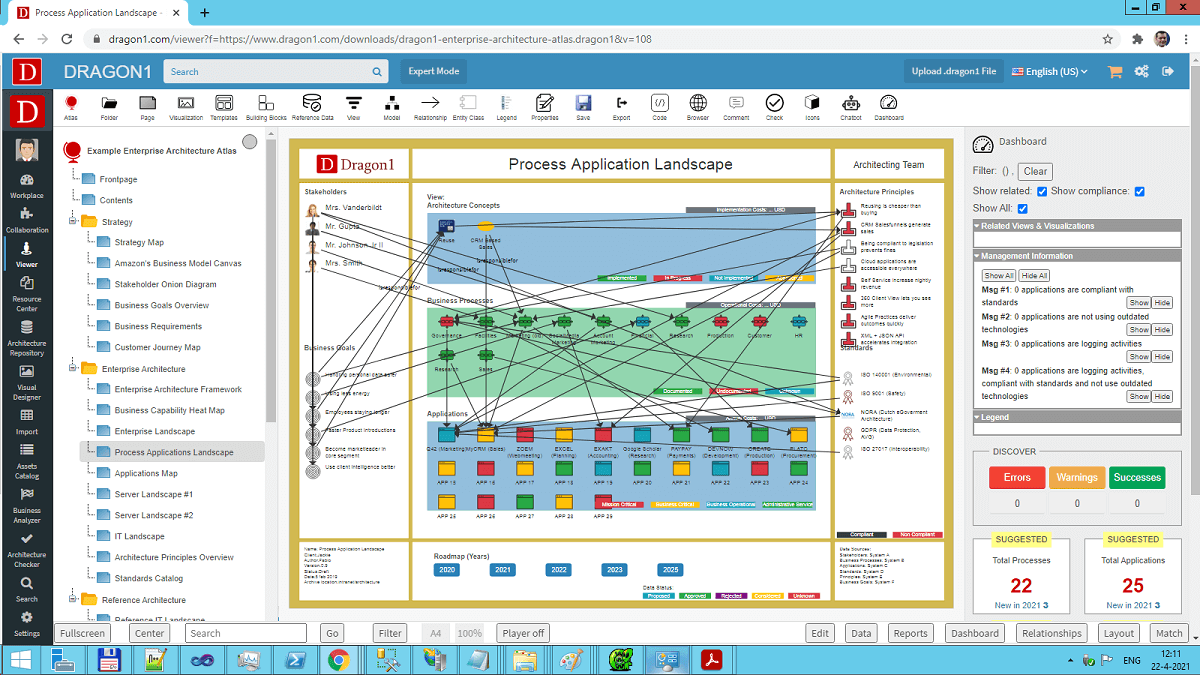
Business architecture is a discipline that defines the enterprise in terms of its business capabilities, value streams, organizational structure, and information assets. It provides a blueprint for understanding how the organization operates and how it can be transformed to achieve its strategic objectives. Business architecture tools support this process by providing a platform for:
Visualizing Business Concepts
Creating and managing business capability maps.
Analyzing Business Performance
Identifying gaps and redundancies in business processes.
Communicating Business Insights
Generating reports and dashboards for stakeholders.
Key Features of Business Architecture Tools
A comprehensive business architecture tool should offer a range of features to support the various aspects of the discipline. These features can be broadly categorized into:
Modeling and Visualization
Capability Modeling: Tools must support the creation and maintenance of capability maps, allowing users to define and categorize business capabilities.
Analysis and Simulation
Gap Analysis: Identifying discrepancies between current and desired states.
Collaboration and Communication
Collaboration Features: Enabling multiple users to work on the same architectural artifacts simultaneously.
Types of Business Architecture Tools
Business architecture tools can be broadly classified into several categories, each with its own strengths and weaknesses:
Dedicated Business Architecture Platforms
These tools are specifically designed for business architecture and offer a comprehensive set of features.
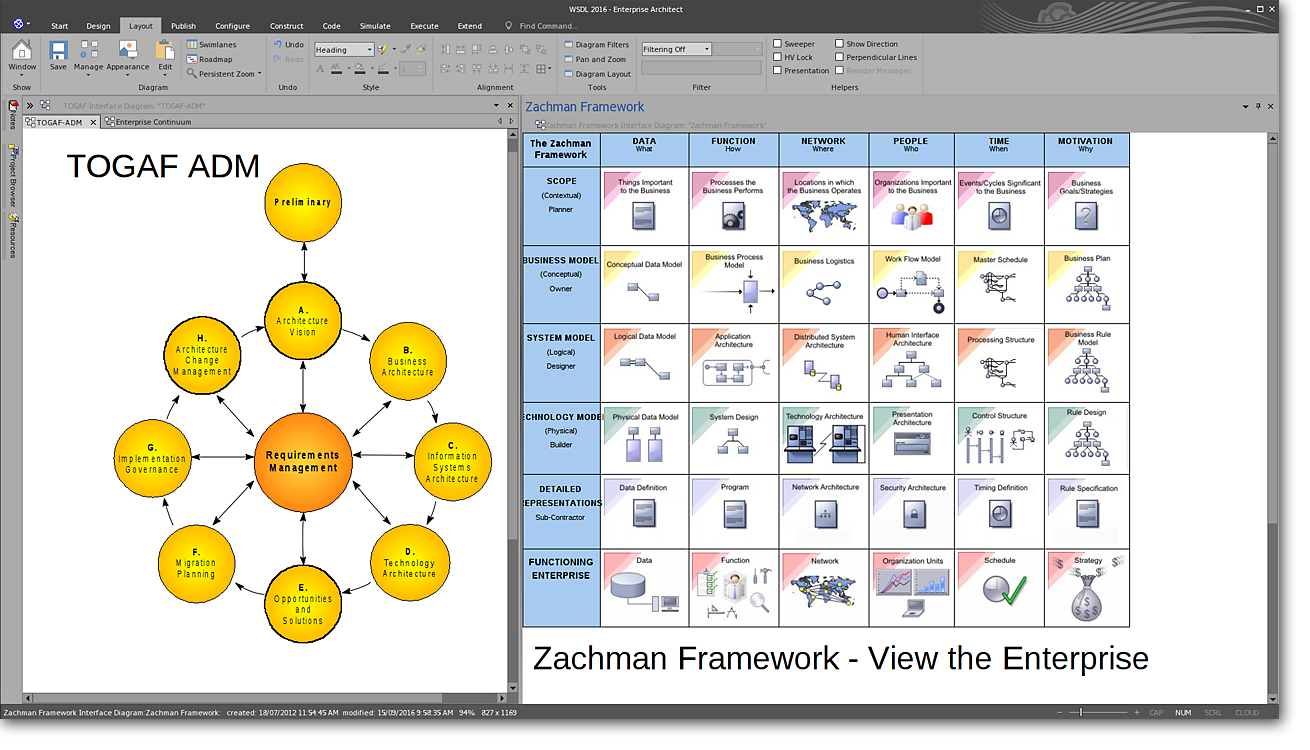
Enterprise Architecture (EA) Tools
EA tools often include business architecture capabilities as part of a broader suite of features.
Business Process Management (BPM) Tools
BPM tools focus on modeling and automating business processes.
Spreadsheet and Diagramming Tools
Tools like Microsoft Excel and Visio can be used for basic business architecture modeling.
Selecting the Right Tool: Key Considerations
Choosing the right business architecture tool is crucial for the success of any initiative. Organizations should consider the following factors:
Business Needs and Requirements
Clearly define the organization’s business architecture goals and objectives.
User Experience and Usability
Choose a tool with an intuitive and user-friendly interface.
Integration and Compatibility
Ensure that the tool can integrate with other enterprise systems and tools.
Vendor Support and Training
Choose a vendor that provides comprehensive support and training.
Cost and Licensing
Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including licensing, implementation, and maintenance.
Scalability and Performance
Ensure that the tool can scale to meet the organization’s growing needs.
The Future of Business Architecture Tools
The field of business architecture is constantly evolving, and so are the tools that support it. Future trends include:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML will be used to automate tasks, analyze data, and generate insights.
Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud-based tools will offer greater flexibility, scalability, and accessibility.
Low-Code/No-Code Platforms
Low-code/no-code platforms will make it easier for business users to create and modify architectural artifacts.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
Tools will provide more advanced collaboration features, such as real-time co-editing and integrated communication channels.
Conclusion
Business architecture tools are essential for organizations seeking to align their strategies with their operational capabilities. By providing a platform for modeling, analyzing, and communicating business insights, these tools enable organizations to make informed decisions and drive strategic execution. Choosing the right tool requires careful consideration of business needs, user experience, integration, and other factors. As technology continues to advance, business architecture tools will become even more powerful and accessible, empowering organizations to navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape.

